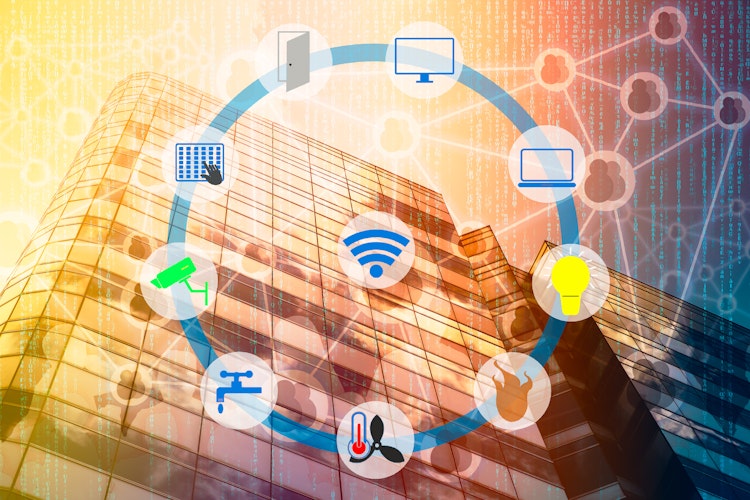
Smart ecosystem: secrets of the successful smart building
As global demand for the smart building grows, how do its various elements integrate and interact to create a seamless environment? One answer is to develop a smart ecosystem, as a new report launched at WORKTECH Berlin 2017 explains
Smart buildings have the potential to use space more efficiently, increase productivity, enhance employee experience, reduce energy costs and support a more flexible work environment.
This is achieved by creating one integrated network that controls all building systems and services, from lighting to access. But how is it all managed behind the scenes?
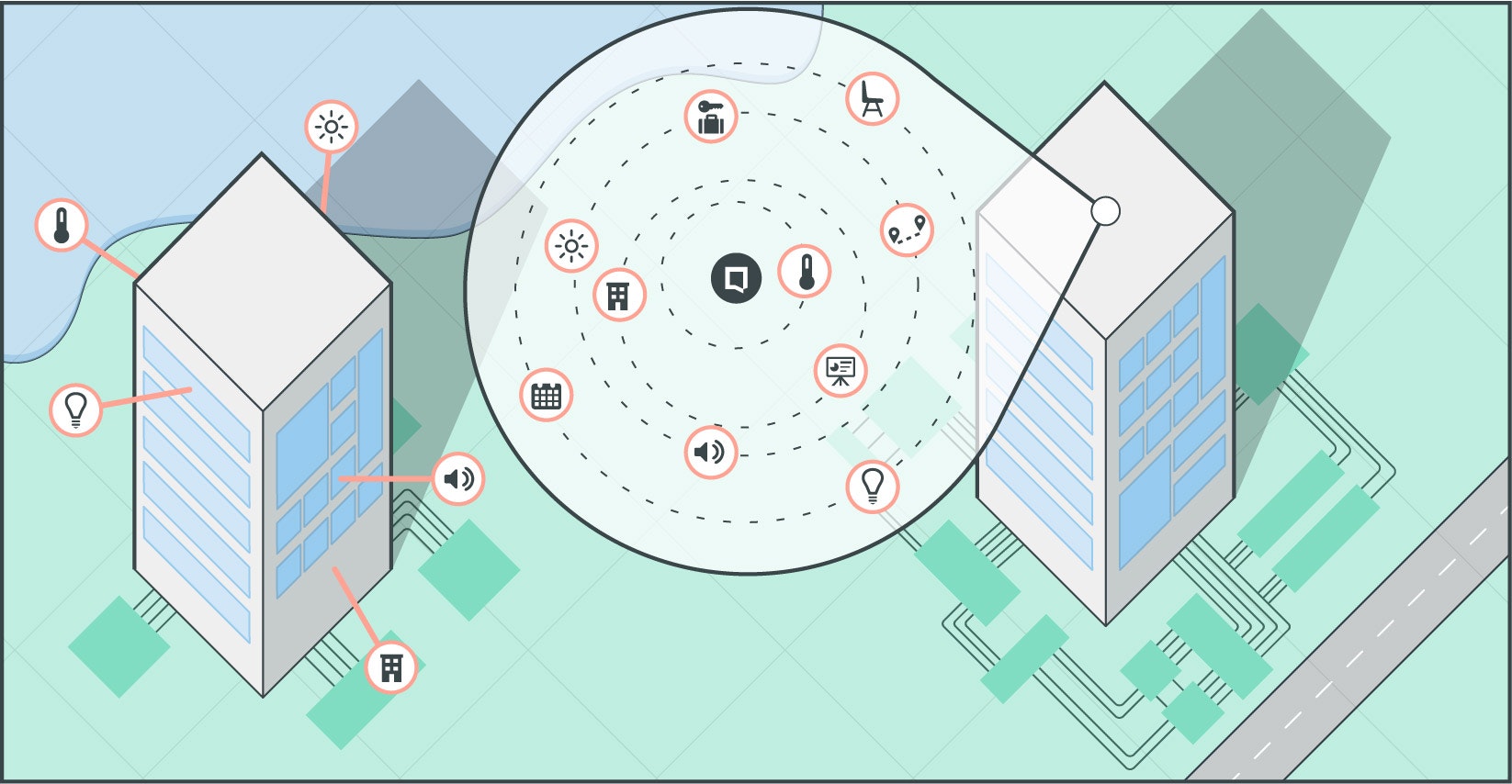
A smart process embraces rapid development of technology and integrates systems providing one user experience
A new report from Dutch technology company Mapiq, given an exclusive launch at WORKTECH Berlin 2017 in partnership with WORKTECH Academy, identifies collaboration as the key to successful smart buildings and describes a software ecosystem (SECO) as a network of collaborative parties that work closely together.
A SECO refers to a set of businesses and their relation to a common software product or service. It consists of software solutions that enable and automate activities and transactions by actors in the ecosystem.
There are five common roles in a SECO identified in the report, derived from academic research: keystone, customer, reseller, niche player and external actor.
These participants are entwined in an interdependent network of organisations that are reliant on each other in terms of components or platforms crucial to the operation of software. Close relationships between organisations improve active engagement of various stakeholders in the development of technology.
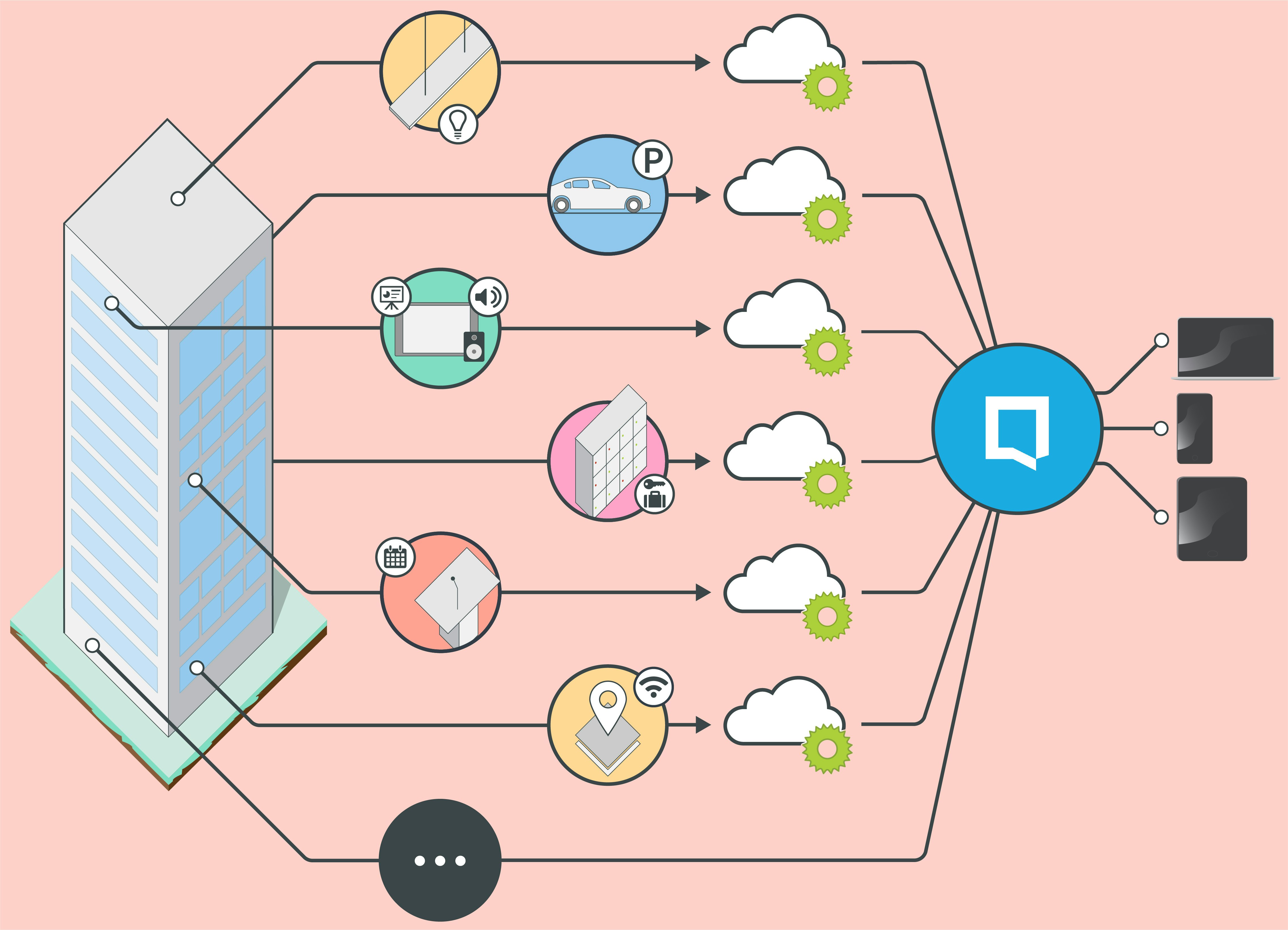
Closer relationships between organisations in an ecosystem improves active engagement of various stakeholders
The report looks at the importance of the relationship between SECO participants and their suppliers, buyers and end-users. It explores the use of Software Operation Knowledge (SOK) as a way for keystones to monitor and manage software operation quality, and determine whether niche player’s software measures up to required standards.
The report emphasises that there must be mutual trust between SECO participants for accurate SOK circulation within ecosystems. Data sharing and a free flow of knowledge is fundamental to creating innovation
The Smart Building Ecosystems report concludes by looking at the shift from a traditional strategy for procuring systems to the future of a fully integrated and holistic approach to realise the full potential of a smart building.








